Yogurt Makers Await FDA Response
The FDA has issued a response – or non-response – to concerns from the International Dairy Foods Association (IDFA).
Last July, the FDA issued a federal, legal definition of yogurt. The new rule upset the IDFA. The association, which represents the nation’s dairy industry, said the FDA’s rule is so outdated and out-of-touch with yogurt makers that popular products could be removed from grocery store shelves. The IDFA objected to the FDA’s rule and submitted an appeal in July 2021 to modernize the yogurt standard of identity (SOI). In December, after not receiving a response, IDFA sent a letter to the FDA commissioner, reiterating the request.
FDA recently issued a “notice of stay” to the IDFA, effectively telling them to keep waiting for a final ruling.
“Yogurt makers have been waiting 40 years for the FDA to update and modernize the yogurt standard of identity,” said Michael Dykes, president and CEO of the IDFA. “Today, the FDA issued a notice telling us to keep waiting — and threw in a whole lot of uncertainty, to boot.”
Adds an IDFA press release: “While a stay is helpful at this stage, IDFA’s efforts to reform the yogurt SOI will continue into an inexplicable fifth decade.”
The FDA first issued a definition of yogurt in 1981. The IDFA has requested a modernized version for decades.
“IDFA remains deeply disappointed in the FDA process that led to the yogurt SOI final rule,” Dykes continues. “After 40 years since FDA first issued standards for yogurt, IDFA and our yogurt members are back to where we started several decades ago, beseeching the FDA to work with yogurt makers to make commonsense updates to a category that has been waiting more than four decades for modernization. Without standards that have been modernized, manufacturers are unable to meet consumer demands for innovative and nutritious yogurt products. With many significant provisions stayed, IDFA will continue to work on the yogurt SOI with an aim to ensure FDA continues to move forward in responding appropriately to IDFA’s objections in a timely manner.”
Read more (IDFA)
- Published in Business
Regulating Home Chefs
The loosely-regulated cottage food industry is growing, as home chefs find it easier than ever to sell handmade meals via online services like WoodSpoon and Shef. These companies are part of the gig economy and trust that chefs will apply for the proper state and local permits to sell food made in a home kitchen. But these apps do not police regulatory compliance, noting only 20-30% of their chefs are licensed.
“In recent months, states have loosened restrictions to make it easier for home cooks to sell products online, but the result is a patchwork of state and local rules, regulations and permit requirements,” reads an article in The New York Times. “Some states allow home cooks to sell only baked goods like bread, cookies or jellies. Others put caps on the amount of money home cooks can make. And other states require the use of licensed facilities, such as commercial kitchens.”
Adds Oren Saar, founder and the chief executive of WoodSpoon: “We are ahead of the regulators, but as long as I keep my customers safe and everything is healthy, there are no issues. We believe our home kitchens are safer than any restaurants.”
As the pandemic ebbs and Americans feel cooking burnout, companies are investing tens of billions into the changing food industry. Alt protein, fast food, food delivery, functional snacks and alt food are all facets of a food industry growing and changing post-pandemic. The New York Times says they’re all making “bets on what, where and how consumers will eat in the coming years.”
Read more (The New York Times)
- Published in Business, Food & Flavor
What’s In a Name? Label & Ad Errors Could Cost Alt Foods Big
As more companies enter the alternative protein marketplace, and more government leaders debate what should be legally considered meat, dairy and egg products, businesses need to be careful with their product names and label and advertising claims.
“It’s hard to think of anything more important than what you’re going to call the product. However, your freedom of invention is not limitless,” says Ricardo Carvajal,a food regulatory lawyer and director at the law firm Hyman, Phelps & McNamara, P.C. “The name must accurately identify or describe the basic nature of the food or its characterizing properties or ingredients. And this can be trickier than it sounds. What’s the composition of the product? What are its essential attributes? What’s it made from? How’s it made?”
Carvajal spoke on labeling and advertising at the Fermentation-Enabled Alternative Protein Innovation conference. Regulations for the young alternative protein industry are broad and confusing, he pointed out. Alternative foods have not been given a “standard of identity” by the FDA – the legal definition that dictates the composition of a food product, how it’s made and its name. Without formal federal direction regarding alternative foods, legislators across the country are making their own rules.
Governing Alt Food
A majority of states have considered regulating the labeling of alternative food products. So far, 32 states have proposed guidelines, and 15 of those have enacted legislation.
“It’s a bit of a smorgasbord in terms of the content of these state laws,” Carvajal adds. “This is going to remain a difficult issue for companies to navigate. If there’s a standard of identity, a federal law, that’s going to take precedence over state laws. But what we’re seeing is an absence of a federal law or a regulation to cover some of these issues or some of these product categories. That’s leaving the door open for the conventional industry to push for laws at the state level.”
This year the USDA plans to issue guidelines for labeling claims on food products made using animal cell culture technology, which will establish nomenclature and labeling requirements for those alternative proteins. The USDA also plans to provide direction on the labeling of plant-based milk alternatives by June 2022.
Carvajal points to the “soy milk saga” as a cautionary example. Milk is a formal FDA standard of identity, defined as ““the lacteal secretion, practically free of colostrum, obtained by the complete milking of one or more healthy cows.” Plant-based milk brands have been sent warning letters by the FDA, arguing a plant product is misbranded as milk. The soy industry has petitioned the FDA to establish soy milk as a common name, but the dairy industry has lobbied aggressively to enforce preserving traditional dairy product names.
Those FDA warning letters can be a big blow to a company — they’re published on the FDA website, so potential investors and customers can review. Letters are monitored by plaintiff’s lawyers, too. These attorneys specialize in suing companies on behalf of consumers, alleging consumers were misled by false claims. “Those actions can be quite expensive to defend,” Carvajal notes.
“Selecting or devising an appropriate name for a product can be a tricky exercise that requires simultaneous consideration of a number of factors,” he says. “The FDA does not view a name as a marketing opportunity.”
Types of Labeling & Advertising Claims
Though there are no formal legal definitions of alternative foods, alt brands do need to follow FDA, FTC and USDA labeling rules. These regulations include:
- Nutrient content (FDA oversight). A nutrient must have an established daily value to make a particular claim. For example, “Excellent source of protein” on a label requires the product to provide 20% of the recommended daily value of protein, while “Good source of protein” requires only 10-19%.
- Health (FDA oversight). This is a tightly-regulated area, Claims that imply a cause-and-effect relationship between a specific nutrient and a disease or health condition require scientific studies on humans. This research can take years to receive FDA approval.
- Structure/function (FDA/FTC oversight). This is the most popular type of claim on a food label because it doesn’t require review or approval in advance of going to market. Examples here are “Protein helps build strong muscles” and “Promotes a healthy immune system.” Still, a structure/function claim must be substantiated.
- Environmental benefit (FTC oversight). Green claims need to comply with the FTC’s Green Guides, which give guidance on environmental marketing claims. Carvajal advises brands to avoid using terms like “eco-friendly” on a product label or in advertising because “they’re impossible to substantiate.” There are a variety of environmental certifications and seals that are better options for a product label.
- Organic (USDA oversight). Organic food must meet USDA standards through the National Organic Program (NOP). Violations result in costly penalties.
- Natural (no official definition). Natural does not have a legal definition — the FDA permits use of “natural” if the food does not contain anything artificial or synthetic. Meanwhile, the USDA views natural as a minimally processed product with no artificial ingredients, with the determination based on the specific product c rather than a category. Carvajal says a natural claim is a “very high risk” for a brand because “the absence of a legally binding definition has enabled plaintiffs lawyers in a wide range of circumstances.”
“You should assume that virtually any claim that you use on labeling or advertising will be subject to regulation of some kind,” he adds. “The requirements that apply might be general in nature or highly specific. So to protect your business, you should have a formal internal review process to ensure that you properly vet all your claims.”
- Published in Business
Food and Beverage Laws Passed in 2021, Part 2
Changes in the global food system influenced the types of laws U.S. legislators passed in 2021. States are loosening the regulations on breweries and wineries, offering more government support to local restaurants, allowing the sale of homemade foods and cracking down on hidden fees from third-party food delivery services.
In our last newsletter, we shared the food and beverage laws passed in 20 states in 2021. The list below completes the balance of the country — Massachusetts to Wyoming.
Massachusetts
HB21 — Allows temporary licenses for nonprofit charitable corporations. Allows alcoholic beverages sold to be donated at no charge to the license holder.
HD1331 — Provides that a license to operate a restaurant may be connected to other on-site premises, even if it is not a grocery store.
SB2475 — Extends to-go cocktail sales through May 1, 2022.
SB2603 — Sets minimum standards for the confinement of chickens, veal calves and pigs, and bans the in-state sale of products that don’t comply. Mandates cage-free conditions for egg-laying hens with welfare enrichments like perches, dust bathing areas, scratching areas and next boxes. The law also expands coverage to egg products and liquid eggs.
SB2841 — Reform state’s franchise laws, allowing a new qualified brewer for craft brewers. Allows craft brewers who produce fewer than 250,000 barrels annually to end their contract with a wholesaler. It repeals the state’s 1971 franchise law, enacted to protect in-state distributors from larger, out-of-state, foreign brewers, during a time when the craft beer industry did not exist.
Michigan
HB4711 — Allows baseball stadiums at Michigan universities to serve alcohol.
SB49 — Allows wineries, breweries and distilleries to operate both an on-premise and off-premise tasting room at the same location.
SB141 — Allows small craft distillers to self-distribute up to 3,000 gallons per year of product to retailers. Also allows craft distillers to ship directly to consumers.
SB142 — Allows a small wine maker to self-distribute directly to retailers.
SB144 — Expands the definition of a mixed spirit drink to allow increased ABV percentage.
SB559 — Amends state liquor code to allow more entertainment complexes to receive liquor licenses; drops number of needed races from seven to two for a motorsports venue to qualify for a liquor license.
Minnesota
SB958 — Raises the sales cap for cottage food sales from $18,000 (formerly the lowest sales cap in the country) to $78,000.
Mississippi
HB562 — Allows online sales of cottage foods.
HB572 — Expands boundaries of resort areas where alcohol can be sold.
HB997 — Authorizes private retailers to obtain wholesaler permits for alcohol sales. Also removes the state’s Department of Revenue as a wholesale distributor of alcohol.
HB1091 — Amends code to increase the alcohol content for alcoholic products. Defines how much product can be produced and sold at a microbrewery.
HB1135 — Allows alcohol delivery from a licensed delivery.
HB1288 — Amends code to allow a charter ship to sell and serve alcohol.
Missouri
HB537 — Allows online sales of cottage foods and removes the $50,000 sales limit on cottage foods.
HB574 — Prohibits inspectors of agricultural grounds or facilities to enforce laws of states other than MIssouri.
SB126 — Legalizes the permanent sales of to-go alcohol. Also expands the sale of alcohol in the state on Sundays.
Montana
HB79 — Provides regulatory clarity for how breweries produce fermented-style beverages, including any alcoholic beverages made by fermentation of malt substitutes, like rice, grain, glucose, sugar or molasses.
HB157 — Removes restrictions for alcohol licensing, allowing brewers and immediate families to both hold a license.
HB226 — Makes permanent the curbside delivery and to-go drink options for licensed retailers established during the Covid-19.
SB199 — Establishes the Montana Local Food Choice Act. The food freedom bill exempts certain homemade or cottage food products from food licensing and inspection regulations. It also expands the types of foods that can be sold.
SB247 — Allows colleges and universities in the state to serve beer and wine at sporting events.
SB320 — Legalizes the home delivery of beer and wine.
Nebraska
LB274 — Amends the Nebraska Liquor Control Act, making permanent licenses to sell to-go alcoholic beverages. Also allows craft breweries and wineries to sell alcoholic beverages at open-air farmers markets.
LB324 — Establishes the Independent Processor Assistance Program, improvising the Nebraska Meat and Poultry Inspection Law. Helps small locker plants make the transition to a federally-inspected facility.
LB396 — Adopts the Nebraska Farm-to-School Program Act, which establishes a structure to facilitate communication between farmers and schools.
Nevada
SB297 — Requires the Council on Food Security to research and develop recommendations on community gardens and urban farms.
SB307 — Prohibits direct-to-consumer (DTC) shipping of alcohol from both in-state and out-of-state breweries, distilleries and retailers. In-state retailers can also make local deliveries from licensed wholesalers. However, DTC wine shipments will still be allowed.
SB320 — Requires food delivery services such as Uber Eats and DoorDash to disclose fees to consumers, breaking down what price is for food, taxes, delivery fee and commission charted to the restaurant. Restaurant committees are limited to 20% of a credit card processing fee during a state of emergency (like the Covid-19 pandemic).
New Hampshire
HB226 — Gives state department of agriculture authority to stop the sale of any produce in violation of state agricultural laws.
HB345 — Establishes a license for wild mushroom harvesters. Allows state department of health and human services to fine people who distribute wild mushrooms without a license.
HB593 — Requires food delivery service to enter into an agreement with a food service establishment before offering delivery service from that restaurant.
SB66 — Allows takeout and delivery of alcoholic beverages.
SB125 — Eases certain regulatory restrictions for a number of beverage manufacturer licenses. Removes limitation on quantity of beer a beverage manufacturer may sell in a day to the public and allows direct-to-consumer shipping to consumers within the state.
SB155 — Allows restaurants to permanently expand dining into a shared space, like a sidewalk or street, with approval from local authorities. This temporary dining space was originally established during the Covid-19 pandemic.
New Jersey
AB1091 — Requires Division of Travel and Tourism to advertise and promote tours of breweries in the State.
AB1478 — Permits theaters with 50 seats or more to apply for liquor license.
AB5906 — Rescinds prohibition on return of certain items purchased from retail food stores during Covid-19 state of emergency. It also provides that future limitations on returns occur during declared public health emergencies.
SB673 — Establishes New Jersey’s first cottage food law (they were the only state in the U.S. without a cottage food law). Allows home-based producers to make food from home rather than a commercial kitchen. These producers must obtain a license every two years, cannot earn more than $50,000 a year and are limited by products that can be sold (though state permission can be granted for additional items).
SB3340 — Expands opportunities for restaurants, bars, distilleries and breweries to operate during the Covid-19 pandemic. Provides outdoor dining space and opens new permits for sales at farmers markets.
SB3364 — Allows certain liquor licenses to acquire alcoholic beverage licenses from a retail food store that is a bankrupt asset.
New Mexico
HM1 — Requests the New Mexico Department of Agriculture to study the economic benefits of regional mobile livestock slaughter units, which would make livestock slaughtering easier for small ranchers.
HB177 — Enacting the Homemade Food Act. Allows anyone in the state to start a cottage food business — and opens sales to be from home and online (cottage food sales were previously limited to events only).
HB255 — Allows restaurants to purchase a liquor license at a more affordable rate ($2,500-$10,000, depending on size) if serving alcohol with dinner. Also allows alcohol deliveries with food.
HB303 — Bans unlawful liquor incentives. No liquor licensee shall accept money or a gift of monetary value to influence the purchase or a certain brand of alcoholic beverage.
SB1 — Allows qualified state food and beverage establishments to claim a temporary gross receipts tax (GRT) deduction on sales of food and beverages from March 2, 2021 through July 1, 2021 as a stimulus incentive.
SB2 — Waives the annual liquor license fees for licensees, aiming to boost businesses hit by the Covid-19 pandemic.
New York
AB952 — Directs the commissioner of agriculture and markets and the commissioner of economic development to work with the state’s land grant university system to produce a report to provide advice, guidance and recommendations on improving the resiliency of the state’s farm and food supply. Also will provide guidance on the related supply chain logistics to address food shortages, food waste and the inability to get New York farm goods to markets that occurred as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic, with the goal of creating permanent solutions beyond the state of emergency to reflect the changing wholesale, retail and consumer marketplace.
AB4613 — Creates a task force on improving urban and rural access to locally produced, healthy foods.
AB5386 — Establishes the New York Soil Health and Climate Resiliency Act to enhance and maintain the health and resilience of agricultural soils. The program will assist farmers in improving the health of their soil. It also establishes a climate resilient farming initiative to promote and encourage farmers to reduce the effects of farming on climate change and to adapt to and mitigate the impact of climate change by improving and maintaining water management systems and soil health.
AB7506 — Requires grease traps at food service establishments be designed to withstand expected loads and prevent unauthorized access, making them safer for the general public.
AB7207 — Authorizes and directs the commissioner of agriculture and markets to conduct a study on urban agriculture, including vertical farming, community gardens and urban farming.
SB1630 — Requires third-party food delivery services to have a valid agreement with a merchant before they advertise, promote or sell the merchant’s products on their platform.
SB2743 — Authorizes the issuance of a temporary retail permit by the state liquor authority to licensees located in a municipality having a population of one million or more persons.
SB6353 — Allows restaurants to utilize municipal spaces like sidewalks and streets for outdoor dining for another year. First granted under an executive order during the Covid-19 pandemic, the law makes restaurant use of public spaces to allow restaurants to recover from the pandemic.
North Carolina
HB4 — Extends ABC permit renewal payment deadlines for bars.
HB890 — Allows consumers to order online and pick-up alcohol from state Alcoholic Beverage Control stores, expands growler sizes from 2 to 4 liters, loosens rules for distillery tours and allows distillers to sell alcohol at festivals.
North Dakota
HB1284 — Modifies special event alcohol permit requirements to remove the rule that persons under 21 years of age must remain out of the area where alcohol is served.
HB1475 — Creates a $10 million agriculture diversification and development fund to provide loans and grants for value-added agriculture businesses in the state.
SB2220 — Moves the sale of Sunday alcohol sales to 8 a.m., the same as the rest of the days of the week in the state..
SB2321 — Allows microberies and taprooms to ship products in-state.
Ohio
HB665 — Increases the amount a county or independent agricultural society receives for operating expenses from a county. Removes caps on junior club membership .
HB669 — Makes to-go alcohol sales permanent.
HB674 — Allows home delivery of alcohol, as long as the beverage is served in an original container.
SB102 — Sweeping liquor reform. Lowers the age for serving alcohol to 18, expands Designated Outdoor Drinking Areas spaces, clarifies that homebrewers are allowed to brew their own drinks, enter them in tasting competitions and share them at local club gatherings.
Oklahoma
HB1032 — Creates the Homemade Food Freedom Act which provides for regulation and oversight for the production, transportation and sale of homemade food products. Now allows almost all types of baked, non-perishable and perishable foods. Also increases sale limits from $20,000 to $75,000, allows direct sales and allows shipment of non-perishable items.
HB2117 — Allows certain communication and interaction via social media by alcohol wholesalers, beer distributors and retailers.
HB2122 — Allows the sale of to-go cocktails, mixed drinks or single-serve wine in a sealed container for off-premise consumption.
HB2277 — Permits licensed alcohol retailers to offer different drink specials at various locations owned and operated under their license, like a happy hour.
HB2380 — Allows customers to self-pour their own beer, wine or mixed beverage from automated machines.
HB2726 — Allows Oklahoma small businesses to offer bottle service to their customers.
SB85 — Authorizes holders of multiple small brewer licenses to sell beer at multiple locations.
SB262 — Requires wine and spirit wholesalers to remit alcohol excise taxes when purchasing alcoholic beverages for sale within the state except for wine shipped by wineries possessing a Winemaker Self-Distribution License.
SB315 — Allows licensed distillers to sell spirits for on- or off-premise consumption on distillery property or in an area connected and controlled by the licensee.
SB385 — Allows retail spirits, wine and beer licensees to host alcoholic beverage tastings.
SB499 — Requires that customer receipts for alcoholic beverages purchased at catered, public and special events include a line item for the 13.5% tax collected.
SB760 — Allows multiple alcohol licensees to designate a common drinking area.
Oregon
HB2111 — Changes name of “Oregon Liquor Control Commission” to “Oregon Liquor and Cannabis Commission.”
HB2264 — Alcohol reform bill. Allows Indian tribe or airline that holds full on-premises sales license to negotiate with Oregon Liquor Control Commission purchase price of distilled liquor for specified sales. Directs Oregon Liquor Control Commission to study alcohol. Changes definition of “malt beverage.” Allows nonprofit organizations to sell alcoholic beverages for up to 45 calendar days per year without license issued by commission. Allows holder of full on-premises sales license to sell, deliver and ship to consumers specified alcoholic beverages for off-premises consumption. Allows holder of limited on-premises sales license to deliver and ship to consumers specific alcoholic beverages for off-premises consumption. Allows holder of off-premises sales license to sell specified alcoholic beverages for off-premises consumption. Allows holder of temporary sales license to ship specified alcoholic beverages to consumer. Repeals license application fee. Allows advertising by liquor store to be visible from outside store. Specifies that retail sales or distillery outlet agent’s deposit with commission is of check and cash receipts. Specifies wine containing more than 16% alcohol by volume is taxed at 10 cents per gallon. Requires manufacturer, purchaser and distributor of alcohol to retain records for three years.
HB2742 — Allows holder of off-premises sales license to sell factory-sealed containers of malt beverages that hold more than seven gallons.
HB2363 — Allows certain holders of temporary event licenses to sell specified alcoholic beverages for on and off-premises consumption at more than one location on licensed premises — or have up to three premises licensed under single temporary sales license and operate for up to 30 day.
HB2395 — Modifies single-use checkout bag prohibition in the state. Changes definition of “recycled paper checkout bag” to include bags that contain non wood renewable fiber.
HB2611 — Permits agricultural building to be used for uses other than uses set forth in definition of “agricultural building” if additional uses are incidental and accessory to defined uses, are personal to farm owner and farm owner’s immediate family or household and do not pose hazard.
HB3361 — Requires third-party food platform to enter into agreement with restaurant before arranging delivery of orders from food place or listing food place on application or website. Requires third-party food platform delivery service to receive written consent from restaurant before arranging for delivery or order from restaurant.
SB806 — Includes “fortified cider” in definition of cider. Allows holder of direct shipper permit to ship up to five cases of wine per month to Oregon residents. Deletes requirement that commission charge application fee for new licenses. Provides that the alcohol commission may allow applicant to defer or waive payment of annual license fee if Governor declares state of emergency.
Pennsylvania
HB425 — Allows a liquor licensee that has closed either permanently or for a long time to sell its liquor license.
HB427 — Gives establishments with liquor licenses a 15% discount (instead of 10%) on the purchase of liquor from the state stores for three years.
SB434 — Alters “sell by” and “best by” dates on milk. Allows processors to apply for Department of Agriculture approval to exceed the current 17 day limit.
Rhode Island
HB5131 — Prohibits a food service establishment from providing a consumer with a single-use plastic straw, unless the consumer requests such a straw.
HB5214 — Eliminates the $10.00 fee requirement for businesses to obtain a sales tax permit.
HB5758 — Establishes the state’s first Cottage Food Law, but only allows farmers to sell homemade products.
SB142 — Allows the sale of alcoholic beverages on New Year’s Day by retail Class A licensees.
SB364 — Entitles dairy farms to the exemptions from taxation already granted to farmland, forestland and open space.
SB555 — Authorizes a Class B liquor license holder to sell to-go alcoholic beverages with take-out food orders (but rule will sunset on March 1, 2022).
SB788 — Prevents third-party food delivery services from using the likeness, registered trademark or any intellectual property belonging to the restaurant to falsely suggest sponsorship or endorsement without the restaurant’s consent.
South Carolina
SB619 — Allows more off-site tasting rooms in the state. Amends 1976 law affecting distilleries, breweries and wineries, to establish off-site “satellite locations” for sale of their products.
South Dakota
HB1109 — Updates state homebrew legislation to include cider as a permissible homemade alcoholic beverage. Allows (in limited quantities) for homemade alcoholic beverages permissible to be sold on licensed premises for certain events, and allows homebrewers to transport homemade alcoholic beverages from their household.
HB1121 — Deregulates the homemade or cottage food market. Repeals requirement that homemade canned goods must be inspected by a third-party authority for pH levels. Replaces lengthy warning that food wasn’t produced in a commercial kitchen and required allergen listing with a shorter summary. Allows sellers to sell their products through third parties without getting a good service license (as long as they aren’t making more than $150,000 a year).
HB1153 — Authorize the Board of Regents to contract for the design and construction of a new dairy research and extension farm on the campus of South Dakota State University, with equipment and furnishings.
Tennessee
HB306 — Extends the Tennessee dairy promotion committee to June 30, 2029.
HB1129 — Adds requirements for farmers to participate in herdshare programs, like maintain owner records, include warning labels on products and notify owners in case of contamination.
HB1514 — Reduces the population threshold (from 925 to 700) to make a municipality eligible to hold a referendum on the sale of alcoholic beverages.
SB17 — Allow breweries to self-distribute 1,800 barrels of beer throughout the state each year without having to go through a wholesaler.
SB269 — Authorizes a delivery service licensee to charge a fee based on a percentage of the sales of the alcoholic beverages or beer being delivered; limits the fee to no more than 10% of the price of each alcoholic beverage sold.
SB299 — Defines “food hall” for purposes of consumption of alcohol on the premises of a food hall; enacts certain requirements governing the operation of a food hall.
SB403 — Requires state to disclose certain information on contracts with wholesalers of alcoholic beverages.
SB591 — Authorizes a person or entity holding liquor license to sell or transfer their alcoholic beverage inventory to another licensee if they’re closing their establishment.
SB681 — Allows to-go alcohol sales for the next two years.
SB705 — Prohibits licensure as a winery direct shipper of in-state or out-of-state wine fulfillment houses.
Texas
HB1024 — Allows permanent sales of to-go beer, wine and mixed drinks for pickup and delivery food orders.
HB1276 — Allows restaurants to sell bulk foods directly to the public.
HB1518 — Loosens alcohol restrictions on Sunday mornings, allowing sales starting at 10 a.m. rather than noon.
HB1755 — Allows customers to take home unopened bottles of wine.
HB1957 — Sets new standards on what can be labeled as a Texas wine. If putting Texas on the wine label, winery must grow majority of grapes (75%-95%) within the state, county and/or vineyard on the label.
HR2002 — Recognizing June 2022 as National Dairy Month in Texas.
SB617 — Allows all food producers to sell food directly to consumers, not just farmers. Limits permit fees.
SB911 — Bans third-party food delivery service from using a restaurant’s trademark or charging a restaurant fees (unless agreed upon in writing). Also protects a restaurant from predatory food delivery services — allows a restaurant to be removed from the third-party delivery services listing if requested, and required third-party delivery services to provide consumers with a means to express concerns with their delivery. Gives restaurants the power to sue a third-party delivery service if it violates the terms. Also prohibits cities and counties from creating interfering regulations than what the state approved.
SB1226 — Allows brewpubs to legally host tastings.
Utah
HB94 — Legalizes microenterprise home kitchens, allowing home chefs to sell their homemade meals.
HB296 — Creates the Utah Soil Health Program.
SB137 — Gives the Utah Department of Alcoholic Beverage Control an additional $4.3 million to raise salaries for its retail clerks, warehouse workers, store managers and assistant managers up to market standards.
SB147 — Prohibits farm owners and operators in the state from confining egg-laying hens to enclosures. Must implement cage-free housing systems by 2025.
HB166 — Criminalizes theft of livestock.
Vermont
HB218 — Expands raw milk sales for producers selling at farm stands and CSA’s in the states.
HB313 — Extends for two years the governor’s executive order to allow curbside pickup and delivery of alcohol.
HB434 — Establishes the Agricultural Innovation Board.
SB20 — Bans the sale of common items containing PFAS (perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances used to make food packaging grease- and water-resistant). The bill takes steps to restrict harmful phthalate and bisphenol chemicals from food packaging.
Virginia
HB1299 — Allows for the sale of to-go alcohol beverages until July 1, 2022.
HB1902 — Prohibits food vendors from using single-use expanded polystyrene food service containers. Requires chain restaurants to stop using such containers by July 1, 2023, and sets the date for compliance by all food vendors as July 1, 2025. A penalty will be inflicted of $50 a day for violators.
HB1973 — Allows nonprofits conducting online fundraisers to sell and ship wine in closed containers as part of a fundraising activity.
HB2068 — Establishes the Local Food and Farming Infrastructure Grant Program. The governor will award the grants based on infrastructure development projects that support local food production and sustainable farming.
HB2302 — Allows farmers markets to be treated as grocery stores during state of emergency and are allowed to remain open as essential businesses during a state of emergency declared by the Governor.
SB1188 — Establishes the Virginia Agriculture Food Assistance Program and Fund for Virginia farmers and food producers to donate, sell, or otherwise provide agriculture products to charitable food assistance organizations.
SB1193 — Establishes the Dairy Producer Margin Coverage Premium Assistance Program. Gives dairy farmers (with a resource management or nutrition management plan) the ability to receive a refund of their annual premium payment paid into the federal program.
SB1428 — Prohibits the Virginia Alcoholic Beverage Control Authority from selling in government stores low alcohol beverage coolers not manufactured by licensed distillers.
SB1471 — Allows the Board of Directors of the Virginia Alcoholic Beverage Control Authority to increase the frequency and duration of outdoor events that sell alcohol. The laws are expected to provide flexibility to restaurants during COVID-19.
Washington
HB1145 — Allows the use of non wood renewable fiber in recycled paper carryout bags.
HB1480 — Allows sale of to-go alcohol products, including cocktail kits and growlers.
HB5362 — Ensuring the funding of agricultural fairs.
SB5022 — Enacts recycling requirements for plastic beverage containers. Bans polystyrene (EPS) products and sets-up opt-in requirements for dining establishments using single-use foodware.
SB5272 — Waives a one-time annual liquor license and cannabis license fee for those establishments for 12 months.
West Virginia
SB 51 — Requires dairy foods processed in the state to be added to the list of items to be purchased by state-funded institutions.
SB 58 — Creates the West Virginia Farm Fresh Dairy Act.
Wisconsin
SB56 — Allows alcohol beverage retailers to make online or phone sales of alcohol beverages, to be picked up by the customers at a designated parking space that is not part of the retail licensed premises.
Wyoming
HB13 — Increases the amount of wine that a licensed out-of-state wine shipper may ship to any one household address. Allows Wyoming consumers to receive up to 12 cases of wine in a 12-month period (the former limit was four cases per year).
HB51 — Establishes grant program to meat processing facilities suffering during the COVID-19 pandemic.
HB54 — Focuses efforts and resources of the Wyoming Business Council on developing slaughter plant options for producers.
HB118 — Allows sale of eggs under the state’s Food Freedom Act.
HB156 — Allows winery permit holder to be issued an off-premise wine permit for a 24-hour period.
HB159 — Allows any liquor license holder — who then obtains an out-of-state shipper’s license — to ship alcohol to Wyoming households. Increases satellite permits for liquor manufacturers from one to two.
HB229 — Allows Wyoming ranchers the choice of selecting lawful forms of animal identification devices. Rejects USDA mandate to only use higher-cost RFID ear tags for livestock.
2022 Alt Meat Trends & Challenges
“The landscape of cell-cultured meat, and even microbially fermented animal products, is a complicated place where futuristic technology, ethics, the law and business are all approaching the unknown together,” reads a Forbes article.
There are at least 60 companies globally now involved with cell- and fermentation-grown meat, and nearly a billion dollars was invested in the field in 2021 alone.
Animal-free meat, though, is facing growing pains. Forbes shares the trends and challenges in the rapidly-growing alternative protein industry. Some of their predictions and observations:
- Accelerator and incubator programs will help new companies start.
- Startups lead the pack, influencing larger companies to invest in their own animal-free lines.
- Truly animal-free options, as companies develop proprietary methods that don’t require animal input.
- Knowledge sharing, the trend that more companies will not gatekeep their intellectual property.
- Production of all “meats,” rather than just beef and chicken. (Companies are developing animal-free foie gras, fish maw and even zebra.)
- Alt breast milk, using stem cells.
- Cheaper products, as the higher prices of alternative proteins keep some consumers away.
- Regulatory challenges, as regulatory agencies debate terminology and labeling requirements.
Read more (Forbes)
- Published in Business
Food and Beverage Laws Passed in 2021
After the Covid-19 pandemic shortened their legislative sessions last year, lawmakers across the 50 states had a productive year in 2021. State leaders were able to pass hundreds of bills relating to food, beverages and food service.
Numerous new laws were aimed at helping restaurants survive — permitting permanent outdoor dining spaces, allowing carryout food services and to-go alcohol sales. Many of these regulations had been enacted in 2020 as temporary, emergency measures to aid restaurateurs, but expired this year.
This year was also big for cottage food laws. As more people experimented in their home kitchens during the pandemic, there was pressure to modernize cottage food laws. Over half the states updated their laws in 2021, regulating sales of homemade food.
Below are the key food, beverage and food service laws passed this year in, alphabetically, Alabama through Maryland. We’ll feature the balance of the states — Massachusetts to Wyoming — in TFA’s next newsletter (January 12, 2022).
Alabama
HB12 — Extends protections granted for cottage food businesses to include roasted coffees and gluten-free baking mixes.
HB539 — Increases the amount of alcohol which breweries and distilleries can sell to customers for off-premise consumption.
SB126 — Allows licensed state businesses to deliver wine, beer and spirits to customers’ homes.
SB160 — An update to Alabama’s cottage food law, SB160 allows for most non-perishable foods to be made in home-based food businesses without commercial licenses (instead of just only baked goods, jams/jellies, dried herbs and candies). It also removes the $20,000 sales limit for home-based food businesses. It also allows online sales and in-state shipping of products.
SB167 — Permits Alabama wineries to sell directly to consumers at special events.
SB294 — Authorizes wine manufacturers to sell directly to retailers without a distributor.
SB397 — Allows opening of wineries in Alabama’s 24 dry counties. The wineries will be allowed to produce and operate in a dry county, but they may not sell on premise.
Alaska
HB22 — Legalizes herd share agreements for the distribution of raw milk in the state.
Arizona
HB2305 — Amends law to allow two or more liquor producers, craft distillers or microbrewery licenses at one location.
HB2753 — States that licensed producers, craft distillers, brewers and farm wineries are subject to rules and exemptions prescribed by the FDA. Exempts production and storage spaces from state regulation.
HB2773 — Allows bars, liquor stores and restaurants to sell cocktails to-go.
HB2884 — Exempts alcohol produced on premise in liquor-licensed businesses from food safety regulation by the Arizona Department of Health Services, which adds rules regarding production, processing, labeling, storing, handling, serving, transportation and inspection. Specifies that this exemption includes microbreweries, farm wineries and/or craft distilleries.
Arkansas
HB118 — Permits the sale of cottage foods over the internet. Interstate sales are permitted if the producer complies with federal food safety regulations.
HB1228 — Allows for municipalities in dry counties to apply to be an entertainment district, just like in wet counties.
HB1370 — Establishes mead as an allowed liquor for a small farm winery — and allows wineries to ship mead. Also allows for mead to be taxed in the same manner as wine.
HB1426 — Establishes the Arkansas Fair Food Delivery Act, stating that a food delivery platform (like UberEats) must have an agreement with a restaurant or facility to take food orders and deliver food prepared.
HB1763 — Allows distilleries to self distribute their own products and allows out-of-state, direct-to-consumer shipments.
HB1845 — Restricts advertising alcohol in microbrewery-restaurants in dry counties.
SB248 — Replaces Arkansas’ cottage food law with the Food Freedom Act. Allows all types of non-perishable foods to be sold almost anywhere without a food safety license and certification, including grocery stores and retail shops.
SB339 — Allows permitted restaurants to sell on-the-go alcoholic beverages.
SB479 — Allows restaurants with alcohol beverage permits to expand outdoor dining without approval of the Alcoholic Beverage Control Division.
SB554 — Authorizes beer wholesalers to distribute certain ready-to-drink products.
SB631 — Authorizes a hard cider manufacturer to deliver hard cider.
California
AB61 — Allows restaurants and bars with alcohol licenses that added temporary, outdoor sidewalk dining spaces during the Covid-19 pandemic to continue serving alcohol in these spaces.
AB239 — Allows wineries to refill wine bottles at off-site tasting rooms, similar to breweries reusing growlers
AB286 — Requires third-party delivery companies to itemize cost breakdowns of delivery transactions to both restaurants and customers.
AB425 — Updates regulations regarding definitions, assessments, fees and funding mechanisms for the Dairy Council of California.
AB831 — Mandates that all labels on cottage food must include the disclaimer “Made in a Home Kitchen” along with the producer’s county and cottage food permit number.
AB941 — Establishes a grant program for counties to apply for farmworker resource centers, supplying farmworkers and their families information on education, housing, payroll, wage rights and health services.
AB962 — Requires the creation of a returnable bottle system in the state by 2024. Allows recyclable bottles to be washed and refilled by beverage producers rather than being crushed for recycling.
AB1144 — Updates California’s outdated cottage food laws, raising sales limit to either $75,000 (Class A permits) or $150,000 (Class B permits) and simplifying the approval process for sampling cottage food products. Also allows homemade food to be sold online.
AB1200 — By 2023, no eatery in California is permitted to distribute or sell food packaging that contains regulated perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances or PFAS. Manufacturers of food packing must use the least toxic alternative when replacing their food packaging. Food packaging includes food or beverage containers, take-out containers, liners, wrappes, eating utensils, straws, disposable plates, bowls and trays.
AB1267 — Allows licensed manufacturers, distributors and sellers of alcoholic beverages to donate a portion of beverage purchases to a nonprofit.
AB1276 — Requires California eateries to only give take-out customers single-use utensils and condiment packets if they ask for them.
AR15 — Establishes Nov. 22 as Kimchi Day in the state.
SB19 — Allows wineries to open additional off-site tasting rooms without applying for a new license (former law allowed for only one off-site tasting room).
SB314 — Allows restaurants and bars that added temporary, outdoor sidewalk dining spaces during the Covid-19 pandemic a one-year grace period to apply for permanent expansion.
SB389 — Allows restaurants and bars to serve to-go alcohol alongside a meal.
SB453 — Establishes an Agricultural Biosecurity Fund specifically for the California State University system’s Agricultural Research Institute. The California State University’s 23 campuses and 8 off-campus branches can then use that fund to apply for grants related to supporting research on agriculture biosecurity, best practices around infectious agents hurting the state’s animal herds and plant crops.
SB517 — Authorizes a licensed beer manufacturer who obtains a beer direct shipper permit to sell and ship beer directly to a resident of the state for personal use.
SB535 — Makes it unlawful to manufacture or sell imitation olive oil in the state. Also restricts using “California Olive Oil” on a label unless 100% of the oil is derived from olives grown in California. The label can also only share that the oil comes from a specific region of California if at least 85% of the olives were grown in that region.
SB721 — Establishes Aug. 24 as California Farmworker Day.
Colorado
HB1027 — Extends sales of to-go alcohol from licensed restaurants and bars to 2026.
HB1162 — The Plastic Pollution Reduction Act, the law bans single-use plastic bags and containers made from polystyrene (styrofoam) for restaurants and other retailers by 2024. All stores will also implement a 10-cent bag fee for plastic and paper bags by 2023.
SB35 — Prohibits third-party restaurant delivery services from cutting pay to a driver to comply with fee limits. Also prohibits third-party delivery services from putting restaurants on their platforms without the eateries’ permission.
SB235 — Sends the Department of Agriculture $5 million for energy efficiency and soil health programs.
SB270 — Allows more Colorado wineries, cideries and distillers to attain a pub license and sell a variety of food in addition to their craft beverage. Current law puts small limits on the amount of craft drink made for a brewery to sell food, leaving out larger Colorado producers.
Connecticut
HB5311 — Enables permitted transporter to sell and serve alcohol on boats, motor vehicles and limousines.
HB6610 — Codifies expanded outdoor dining, allowing municipalities to close off streets and sidewalks for outdoor restaurant dining space.
SB894 — Allows patrons to pour their own alcoholic drinks at restaurants and bars. Will allow self-pour automated systems to be used in the state’s dining establishments.
HB6580 — Expands food agricultural literacy programs of study and community outreach, by increasing certification, education and extension programs with rural suburban and urban farms for students in grades Kindergarten through 12th grade.
Delaware
HB1 — Allows restaurants to continue selling to-go alcohol beverages. The bill also allows restaurants and bars to continue using outdoor dining spaces originally used during the Covid-19 pandemic.
HB46 — Allows brewery-pub and microbrewery license holders to brew, bottle and sell hard seltzers and other fermented beverages made from malt substitutes. Also includes a specific tax on fermented beverages.
HB143 — Reduces the amount of licensed taprooms to only one taproom within a ½ mile from another taproom.
HB212 — Increases minimum thickness for plastic bags (used by grocery stores and restaurants) to qualify as a reusable bag from 2.25 mils to 10 mils.
SB46 — Allows wedding venues and event centers licensed as bottle clubs to allow customers to bring alcoholic beverages on premise.
Florida
HB751 — Authorizes issuance of special licenses to mobile food vehicles to sell alcohol beverages within certain areas.
HB1647 — Allows more Orlando eateries to sell alcohol. Allows eateries with a smaller footprint (80-person capacity; formerly 150-person capacity) to sell beer, wine and spirits in six additional Orlando Main Street Districts.
SB46 — Increases production limits for distilleries from 75,000 gallons a year to 250,000 gallons. Eliminates the “six bottles per person per brand per year” requirement. Also allows craft distilleries to qualify for a vendor’s license to conduct tastings at Florida’s fairs, trade shows, farmers markets, expositions and festivals.
SB148 — Authorizes restaurants or bars also holding a public food service license to sell or deliver alcoholic beverages in sealed, to-go containers.
SB628 — Establishes a new program, the Urban Agriculture Pilot Project, to distinguish between traditional rural farms and emerging urban farms. Exempts farm equipment used in urban agriculture from being stored in certain boundaries.
SB663 — Updates Florida’s cottage food law to allow shipping of products, and raises the sales limit for shipped cottage food from $50,000 to $250,000. The bill also prevents counties or cities from banning cottage food businesses (Ed. note: Florida’s largest county, Miami-Dade, prohibits cottage food businesses).
SR2041 — Establishes a Food Waste Prevention Week in the state to acknowledge the importance of conserving food and preventing food waste.
Georgia
HB273 — Allows local municipalities to pass an ordinance, resolution or referendum election to authorize allowing a liquor store to open in their jurisdiction
HB392 — Allows a person to have a mixed cocktail or draft beer from the hotel delivered to their room by a hotel employee.
HB498 — Expands eligibility requirements for the state’s tax exemption for agricultural equipment and farm products. Any family-owned farm entity (defined as two or more unrelated, family-owned farms) can now share equipment, land and labor without losing ad valorem tax exemptions enjoyed by stand-alone family farms.
HB676 — Creates a legislative advisory committee on farmers’ markets (Farmers’ Markets Legislative Advisory Committee), made up of five members from the state’s Senate and House.
SR155 — Recognized February 17 as State Restaurant Day.
SB219 — Permits small brewers to sell alcohol for consumption on their premise. Allows state’s breweries to transfer beer between locations.
SB236 — Extends the Covid-era rule that allows restaurants to sell to-go alcohol.
Hawaii
HB817 — Requires state agencies to purchase an increasing amount of locally grown food.
HB237 — Earmarks $350,000 to the department of agriculture for the mitigation and control of the two-lined spittlebug, which has damaged nearly 2,000-acres of pasture land.
SB263 — Establishes a “Hawaii Made” program and trademark, to promote Hawaiian-made products.
Idaho
HB51 — Amends existing law to provide nutrient management standards on dairy farms. Allows dairy farmers the option of using phosphorus nutrients.
HB232 — Changes the distribution of tax on high-alcohol-content beer from the state wine commission to the state hop growers commission, helping promote the craft industry.
Illinois
HB2620 — Allows small breweries, meaderies and winemakers to distribute their products to local bars, grocery stores and liquor stores directly rather than through a third party.
HB3490 — Amends Illinois Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, which says, if a restaurant includes milk as a default beverage in a kid’s meal, the drink must be dairy milk and contain no more than 130 calories per container or serving.
HB3495 — The Brewers Economic Equity & Relief Act, allows for limited brewpub self-distribution, permanent delivery for small alcohol producers, direct-to-consumer shipping for in-state and out-of-state brewers and distillers and self-distribution for manufacturers producing more than one type of alcohol.
HR33 — Creates the Illinois Good Food Purchasing Policy Task Force to study the current procurement of food within the state and explore how Good Food Purchasing can be implemented to maximize the procurement of healthy foods that are sustainably, locally and equitably sourced.
HR46 — Urges the Illinois Department of Agriculture to study the effects and the types of land loss to Black farmers. Calls for state support and capacity building for Black farming communities across the state and a dedication to helping grow agriculture in rural, urban, and suburban areas.
HR117 — Urges the United States Department of Agriculture and the United States Department of Commerce to increase the exportation of Illinois dairy products to other nations.
SB2007 — The Home-to-Market Act, updates the state’s Illinois Cottage Food Law. Expands sales avenues for cottage food producers, allowing sales at fairs, festivals, home sales, pick-up, delivery and shipping (cottage food was previously only allowed to be sold at farmers markets).
Indiana
HB1396 — Updates many of Indiana’s outdated alcohol laws, some from the Prohibition Era. Amended various sections of Indiana’s alcohol code impacting permittees, trade regulation and other various definitions.
HB2773 — Allows bars, liquor stores and restaurants to permanently sell to-go alcohol orders, originally allowed temporarily during the Covid-19 pandemic.
SB144 — Allows bulk wine purchasing limits for farm wineries to apply only to wine sold directly to a consumer and not to wine sold through a wholesaler. Also allows the holder of an artisan distiller permit to also hold a distiller’s permit.
SB185 — Creates a working group made up of industry organizations, food safety experts, Indiana State Department of Health, Indiana State Board of Animal Health and Indiana State Department of Agriculture to submit recommendations to the state concerning home-based vendors and cottage food laws.
Iowa
HB384 — Updates rules regarding alcohol licenses. Lengthens the hours of sale for alcoholic beverages on Sunday.
HF766 — Allows home delivery of alcoholic beverages from bars and restaurants by third-party delivery services, such as Uber or DoorDash.
Kansas
HB2137 — Allows bars, liquor stores and restaurants to permanently sell to-go alcohol orders, originally allowed temporarily during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Kentucky
HR3 — Recognizes March 23 as Agricultural Day in the state.
HR19 — Recognizes June as Dairy Month, honoring the state’s dairy workers.
SB15 — Allows a microbrewery licensee to sell and deliver up to 2,500 barrels of product to any retail licensee and to set forth terms of contracts between microbrewers and distributors.
SB67 — Allows bars, liquor stores and restaurants to permanently sell to-go alcohol orders, originally allowed temporarily during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Louisiana
HB192 — Authorizes credit card payment to manufacturers and wholesale dealers of alcoholic beverages (when previously cash was only allowed).
HB219 — Allows the delivery of ready-to-drink alcohol beverages (sold in manufacturer sealed containers), allowing brewers with a brewing facility to self-distribute.
HB269 — Allows authorized state employees to destroy meat, seafood, poultry, vegetables, fruit or other perishable food of foreign origin which are subject of a current import ban from the federal government.
HB291 — Allows self-distribution to any brewer who operates a brewing facility in the state.
HB706 — Adds microwinery to microdistillery permits.
HR104 — Designates May 19, 2021, as Louisiana Craft Brewers’ Day in the state.
HR210 — Authorizes a state subcommittee to study and make recommendations to the government on the regulation of the growing craft brewing industry in the state.
Maine
SB133 — Clarifies that licensed Maine manufacturers of spirits, wine, malt liquor and low-alcohol spirits products may sell and ship their products to a person located in another state.
SB205 — Allows bars and restaurants to permanently sell to-go alcohol orders through take-out and delivery services if the liquor is accompanied by a food order. Also temporarily permits licensed Maine distilleries that operate tasting rooms but do not operate licensed on-premise retail to sell spirits through take-out and delivery services accompanied by a food order.
SB306 — Temporarily waives certain requirements for relicensing for restaurants that serve liquor to help food establishments during the Covid-19 pandemic.
SB307 — Allows all Maine alcohol manufacturers to sell directly to out-of-state consumers (current law only allows wine to be sold out-of-state).
SB479 — Amends definition of “low-alcohol spirits product” by raising the maximum alcohol level of a low-alcohol spirits product from 8% to 15%.
SB630 — Prohibits shelf-stable products from being sold as cider. Products that do not require refrigeration or are heat-treated cannot be labeled as cider.
SB636 — Establishes the Local Foods Fund, which helps schools purchase produce and other minimally processed foods from local farmers and producers.
SB822 — An act affirming that food seeds are a necessity in the state.
Maryland
HB185 — Prohibits an alcoholic beverages license holder from requiring that an individual buy more than one bottle, container or other serving of alcohol at a time.
HB264 — Requires entities that generate at least two tons of organic waste per week to arrange for disposal alternatives, like reduction, donation, animal feed or composting.
HB269 — Establishes the Urban Agriculture Grant Program in the Department of Agriculture to increase the viability of urban farming and improve access to urban-grown foods.
HB 555 — Repeals a prohibition on allowing drugstores to apply for a liquor license.
HB1232 — Codifies emergency orders to grant permanent to-go delivery of alcohol and online shipment privileges.
SB205 — Authorizes local alcoholic beverage licensing boards to temporarily allow restaurants and bars to sell to-go alcoholic beverages. Also requires Maryland’s Alcohol and Tobacco Commission and the Maryland Department of Health to study expanding alcohol access.
SB821 — Codifies the governor’s 2020 executive order to grant alcohol delivery and shipment. Also allows permitting to serve alcohol at off-premise, special events.
The Regulatory Landscape
Collaboration with regulators, not confrontation, is the recommended course of action for fermenters, experts suggest.
“Producers are speaking one language and regulators are speaking another,” says Abigail Snyder, assistant professor of microbial food safety at Cornell University. “Producers are like ‘Hey, this has been produced forever and it has a history of safe production!’ That’s not super meaningful for regulators. Regulators are used to this codified framework that is not necessarily built around fermented foods. There’s a middle ground.”
Snyder spoke with a panel of experts on health and safety regulations during TFA’s conference, FERMENTATION 2021. The consensus: food regulations exist to protect the consumer, but complying with myriad national, state and local laws can be difficult and frustrating to navigate, especially for a fermented food or beverage that utilizes novel food processes.
“Don’t be afraid, don’t feel like you’re going to tick off the inspector,” says Adam Inman, assistant program manager for the Kansas Department of Agriculture Food Safety & Lodging Program. He advises producers to always ask regulators for help. “Even if we start with your recipe and your process and we just document that, that can go a long way as a starting point.”
Jonathan Wheeler, coordinator for special processes at retail for the South Carolina Department of Health & Environmental Control, says if you’re dealing with a regulator unfamiliar with fermentation, ask for a supervisor. Wheeler manages South Carolina’s team of 80-90 regulators and points out that a health inspection should be an education opportunity for the regulator, too.
“We are partners on the same team, just in different roles,” Wheeler says. “Our approach in South Carolina has been driven by the need to educate as well as regulate. You have a voice, it’s part of collaboration and inspectors…are open to input [from producers].”
Still, compliance is not without its challenges.
Soirée-Leone, writer, homesteader and local food advocate, says that food inspection is one of the biggest challenges for smaller producers — especially in rural areas, where resources can be limited. For example, in Tennessee where she lives, home-based food businesses can sell their goods at farmers markets, as long as those items don’t need to be refrigerated. But there’s no rule for food that needs to be frozen,, so producers are allowed by the health department to sell popsicles.
“It’s very challenging, and a lot of people get very frustrated in the process,” she says.
Erin Leigh DiCaprio, assistant professor of cooperative extension at University of California, Davis, notes that regulations differ from state to state — a ferment produced under cottage food laws in one state could need a processed food license in another. She points out every state or county has an extension educator like herself who has the needed technical expertise to work with producers and regulators. DiCaprio specifically works with smaller-scale processors to navigate regulations in California.
Could the U.S. learn from other countries?In Korea, Japan and China, fermented foods and drinks are common, yet regulations are minimal.
“There’s a cultural aspect there… not necessarily advocating eliminating regulations but saying that a culture — and no pun intended in this case — but a culture that’s been used to eating fermented foods for years and had no negative impact. Is there some education to be learned from that?” questions Neal Vitale, the moderator and executive director of TFA.
“We should not be as regulators in a position of trying to jam fermentation processes… into a mold where they all look the same — because they don’t,” Wheeler says. “Educate me as how you want that process to look.”
- Published in Business
Definition & History of Fermentation
“Human civilization simply would not have been possible without fermented foods and beverages…we’re here today because fermented foods have been popular for humans for at least 10,000 years,” says Bob Hutkins, professor of food science at the University of Nebraska (and a recent addition to TFA’s Advisory Board).
Hutkins was the opening keynote speaker at FERMENTATION 2021, The Fermentation Association’s first international conference. His presentation explored the history, definition and health benefits of fermented foods.
Cultured History
The topic of fermentation extends to evolution, archaeology, science and even the larger food industry.
“The discipline of microbiology began with fermentation, all the early microbiologists studied fermentation,” Hutkins says.
Louis Pasteur patented his eponymous process, developed to improve the quality of wine at Napoleon III’s request. The microbes studied back then — lactococcus, lactobacillus and saccharomyces — remain the most studied strains.
“What interested those early microbiologists — namely how to improve food and beverage fermentation, how to improve their productivity, their nutrition — are the very same things that interest 21st century fermentation scientists,” Hutkins says.
Hutkins is the author of one of the books considered gospel in the industry, “Microbiology and Technology of Fermented Foods.” He says that fermented foods defined the food industry. In its early days, it was small-scale, traditional food production that “we call a craft industry now.” At the time, food safety wasn’t recognized as a microbiological problem.
Today’s modern food industry manufactures on a large-scale in high throughput factories withmany automated processes. Food safety is a priority and highly regulated. And, thanks to developments in gene sequencing, many fermented products are made with starter cultures selected for their individual traits.
“But I would say that there’s been kind of a merging between these traditional and modern approaches to manufacturing fermented foods, where we’re all concerned about time sensitivity, excluding contaminants, making sure that we have consistent quality, safety is a vital concern and extensive culture knowledge,” Hutkins says.
Defining & Demystifying
Fermentation — “the original shelf-life foods” — is experiencing a major moment. “Fermented foods in 2021 check all the topics” of popular food genres: artisanal, local, organic, natural, healthy, flavorful, sustainable, entrepreneurial, innovative, hip and holistic. “They continue to be one of the most popular food categories,” Hutkins continues.
Interest in fermentation is reaching beyond scientists, to nutritionists and clinicians. But Hutkins says he’s still surprised to learn how many professionals don’t understand fermentation. To address the confusion, a panel of interdisciplinary scientists created a global definition of fermented foods in March 2021.
“Fermentation was defined with these kind of geeky terms that I don’t know that they mean very much to anybody,” he says.
The textbook biochemical definition of fermentation that a microbiologist learns in Biochemistry 101 doesn’t work for a nutritionist or clinician focusing on fermentation’s health benefits. The panel, which spent a year coming to a consensus, wanted a definition that would simply illustrate “raw food being converted by microbes into a fermented food.” The new definition, published in the the journal Nature and released in conjunction with the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP), reads: “Foods made through desired microbial growth and enzymatic conversions of food components.”
Fermentation in 2022
Hutkins predicts 2022 will see more studies addressing whether there are clinical health benefits from eating fermented foods. The groundbreaking study on fermented foods at Stanford was important. It found that a diet high in fermented foods increases microbiome diversity, lowers inflammation, and improves immune response. But research like this is expensive, so randomized control trials are few.
Fermented foods could also make their way into dietary guidelines.
“Fermented foods, including those that contain live microbes, should be included as part of a healthy diet,” Hutkins says.
- Published in Food & Flavor, Science
Measuring and Monitoring Fermented Food Microbiomes
Analyzing the microbiome of a fermented food will help manage product quality and identify the microbes that make up the microscopic life. Though diagnostic techniques are still developing, they’re getting cheaper and faster.
“Why should we measure the microbial composition of fermented foods? If you can make a great batch of kimchi or make awesome sourdough bread, who cares what microbes are there,” says Ben Wolfe, PhD, associate professor at Tufts University. “But when things go bad, which they do sometimes when you’re making a fermented food, having that microbial knowledge is essential so you can figure out if a microbe is the cause.”
Wolfe and Maria Marco, PhD, professor at University of California, Davis, presented on Measuring and Monitoring Fermented Food Microbiomes during a TFA webinar. Both are members of the TFA Advisory Board. During the joint presentation, the two gave an overview on microbiome analysis techniques, such as culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches.
Measuring Microbial Composition
Wolfe says there are three reasons to measure the microbial composition of fermented foods: baseline knowledge, quality control and labelling details.
“Just telling you what is in that microbial black box that’s in your fermented food that can maybe be really useful for thinking about how you could potentially manipulate that system in the future,” he says.
What can you measure in a fermented food? First there’s structure, which can determine the number of species, abundance of microbes and the different types. And second is function, which can suggest how the food will taste, gauge how quickly it will acidify and help identify known quality issues.
Studying these microorganisms — unseen by the naked eye — is done most successfully through plating in petri dishes. This technique was developed in the late 1800s
“This allowed us to study microorganisms at a single cell level to grow them in the laboratory and to really begin to understand them in depth,” Marco says. “This culture-based method, it remains the gold standard in microbiology today.”
However, there’s been a “plating bias since the development of the petri dish,” she says. Science has focused on only a select few microbes, “giving us a very narrow view of microbial life.” Fewer than 1% of all microbes on earth are known.
The microbes in fermented foods and pathogens have been studied extensively.“Over these 150 years we have now a much better understanding of the processes needed to make fermented foods, not just which microbes are these but what is their metabolism and how does that metabolism change the food to give the specific sensory safety health properties of the final product,” she says
Marco and Wolfe both shared applications of these testing techniques from research at their respective universities.
Application: Olives
At UC Davis, Marco and her colleagues studied fermented olives. Using culture-based methods, they found that the microbial populations in the olives change over time. When the fruits are first submerged for fermentation, there’s a low number of lactic acid bacteria on them — but within 15 days, these microbes bloom to 10-100 million cells per gram.
Marco was called back to the same olive plant in 2008 because of a massive spoilage event. The olives smelled and tasted the same, but had lost their firmness.
Using a culture-independent method to further study what microbes were on the defective olives, she discovered a different microbiota than on normal ones, with more bacteria and yeast.
The culprit was a yeast.“Fermented food spoilage caused by yeast is difficult to prevent,” Marco says. “New approaches are needed.”
Application: Sourdough
At Tufts, Wolfe was one of the leaders on a team of scientists from four different universities that studied 500 sourdough starters with an aim to determine microbial diversity. Starters from four continents were examined in the first sourdough study encompassing a large geographic region.
The research team identified a large diversity among the starters, attributed to acetic acid bacteria. They also found geography doesn’t influence sourdough flavor.
“Everyone talks about how San Francisco sourdough is the best, which it is really great, but in our study we found no evidence that that’s driven by some special community of microbes in San Francisco,” Wolfe said. “You can find the exact same sourdough biodiversity based on our microbiome sequencing in San Francisco that you can find here in Boston or you could find in France or in any part of the world, really.”
Wolfe and Marco will return for another TFA webinar on July 14, Managing Microbiomes to Control Quality.
- Published in Science
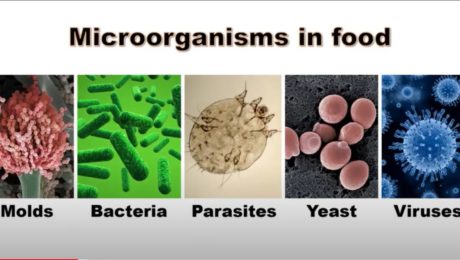
The Safety of Fermented Food
Thanks to lactic acid — which kills harmful bacteria during fermentation — fermented foods are arguably among the safest foods that humans eat. But if critical errors are made, there is the risk of food safety hazards.
“When we talk about fruit and vegetable ferments, there is a very long history of microbial safety with traditionally fermented fruits and vegetables,” says Erin DiCaprio, extension specialist at University of California, Davis, Department of Food Science and Technology. “While outbreaks associated with fermented fruits and vegetables are rare, vegetable and fruit fermentation is not without risk.”
DiCaprio, a food safety expert, detailed proper food safety protocols during a webinar for EATLAC, a UC Davis project putting scientific knowledge and research behind fermentation. DiCaprio shared two documented instances of fermented foods causing a foodborne illness, both from small-scale batches of kimchi. But she emphasized that, when all food safety concerns are mitigated, fermented foods do not pose a risk.
“From the food microbiology standpoint, bacteria really are the most important group of microorganisms because bacteria, certain types of bacteria, are a food safety concern,” she adds. “There are many different types of bacteria that contribute to food spoilage and, of course, there are specific types of bacteria that are used beneficially for fermentation.”
What happens during fermentation that makes food safe? Lactic acid bacteria are created, which convert sugars into lactic acid, acetic acid and CO2. Those antimicrobial compounds help fight off pathogens, competing with other microbes for nutrition sources.
Biological hazards — bacteria, viruses and parasites that can cause foodborne illnesses — are the biggest concerns. Botulism, E. coli and salmonella are the main hazards for fermented foods. Botulism can form in oxygen-free conditions if a fermentation is not successful and acid levels are too low. E. coli and salmonella form when sanitation practices are not followed.
“Commercially, when someone is developing a valid fermentation process, they are typically going to be looking to see that sufficient acid is produced during fermentation, to inactivate some of these acid tolerant (bacteria),” DiCaprio says. “Our traditional vegetable fermentations — things like fermented cucumber, sauerkraut, kimchi — they’ve all been shown to produce sufficient acid to inactivate the sugar toxin producing e-coli, so from a safety standpoint, sufficient acid production is the critical control point for ensuring the safety of a fermented fruit or vegetable. “
There are seven critical factors to keep a ferment safe:
- High-quality, raw ingredients. “If there are a high number of spoilage microorganisms to start with, it will be really difficult for the lactic acid bacteria to dominate the fermentation,” DiCaprio says.
- Research-based recipe. Following a tested recipe ensures the proper balance of ingredients to keep the food safe.
- Proper sanitation. Cleaning of all utensils and surfaces ensures no pathogens will contaminate the food. This mitigates cross-contamination risk, too.
- Preparation of ingredients. Food particles should be uniform in size, either cut in small slices or shredded. Smaller pieces release more water and nutrients, promoting the growth of lactic acid bacteria.
- Salt concentration. Lactic acid bacteria thrive in a salt brine. The key amount: anywhere from 1-15% salt brine by weight of the ferment.
- Appropriate temperature. A temperature between 65-75 degrees fahrenheit is ideal to keep spoilage microorganisms at bay.
- Adequate time. “It takes a while for significant acid to be produced, so be patient and follow the directions in the recipe,” DiCaprio advises. Most fruit and vegetable ferments take 3-6 weeks to be completed.
- 1
- 2